Welcome to the second in our 4-part blog series on program and project governance. In the first post, we discussed the differences between programs and projects. In this post, we highlight the importance of defining rules, procedures, and policies that determine how programs and projects are controlled, managed, and overseen, and discuss some of the key considerations when setting up program and project governance in your organization.

Key Aspects of Program and Project Governance:
- A set of structures, committees, teams, rules, procedures, and policies that determine how programs and projects are controlled, managed, and overseen
- Enables and promotes good, timely decision-making
- Reduces risk
According to this Harvard Business Review article, by Paul Rogers and Marcia Blenko, partners at Bain & Company, “making good decisions and making them happen quickly are the hallmarks of high-performing organizations.” For capital investments especially, but even for operational initiatives, good decisions start with program and project governance. Programs and projects must have proper oversight and accountability, they must align with the corporate strategy and business goals, and the governance must span the program and project lifecycle.
Establishing a governance plan lays the groundwork for order and success. It creates a guide for the decision-making process, and it determines what will happen within the lifecycle of the program and project, when and how it will happen, and who is responsible. There is no one-size-fits-all program or project governance structure that can be used by all companies.
Successful program governance provides the following benefits:
- Increases efficiency and reduces risk
- Establishes a framework for managing issues, opportunities, risks, and competing priorities
- Helps to focus resources across an organization to meet strategic business goals
Key considerations for your organization before you start a program or project:
- Is effective project governance in place?
- Have governing bodies been defined?
- Have the rules, procedures, and policies that determine how projects are controlled, managed, and overseen been defined?
- Have decision-making rights been defined and communicated?
- Is there alignment as to who and how decisions are made?
- Are project-related decisions being made in a timely manner?
When analyzing the answers to big questions like these, don’t hesitate to take action where improvements can be made. If needed, establish, reboot, and/or communicate key components of effective project governance. To increase the likelihood of success, it’s critical to get alignment on these items before starting a program or project:
- Steering Committee
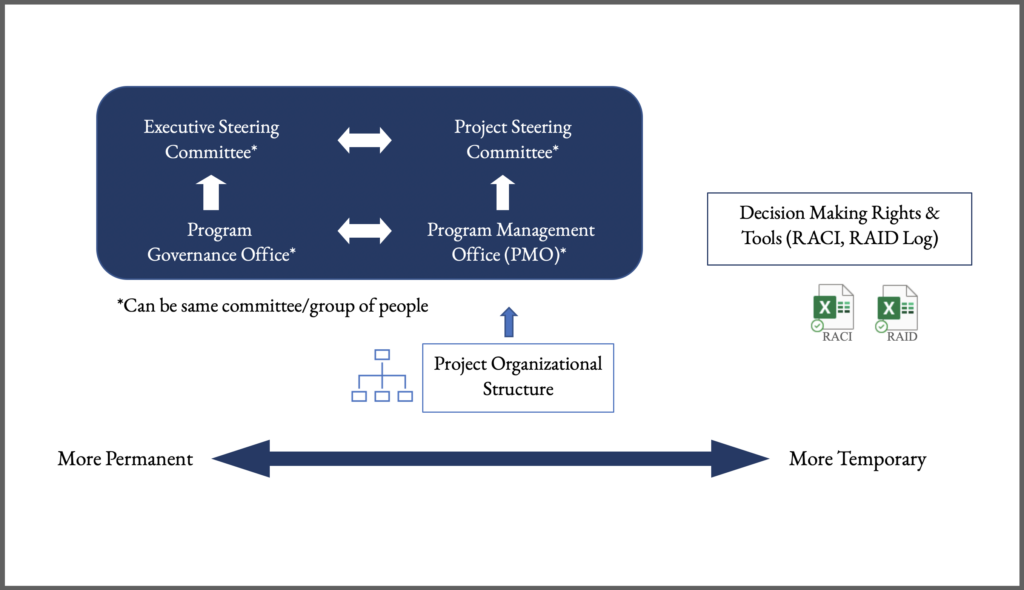
- Project Management Office (PMO)
- Project Organizational Structure
- Decision Making Rights
- RACI
- RAID Log
- Reporting & Status Management
In conclusion, program governance is a crucial aspect of project management that ensures the overall success of an organization’s initiatives. It involves a structured framework and set of processes that govern the planning, execution, and monitoring of multiple projects under one program. In the next part of this series, we will dive deeper into the key components of program governance and how they can positively impact project outcomes. More specifically, we will discuss the three pillars of project governance:
- Project Structure – should be fit-for-purpose
- People – the right people in the right roles
- Information – timely reporting and communication
Send us a note if you have questions on project governance that we can address in our ongoing blog series. Look for our next post in the series soon.
——————
Here are links to all 4 blog posts in this governance series: Part I: Understanding Programs vs. Projects | Part II: Defining Rules, Procedures, and Policies | Part III: Defining Committees, Bodies, and Structures | Part IV: Decision-making Rights and Tools




